Ryugu: Asteroid Samples Continue to Shed Light on Solar System History

© IPGP
Samples of asteroid Ryugu analysed at IPGP
Nearly two years after Japanese mission Hayabusa2 returned to Earth, samples from asteroid Ryugu continue to reveal valuable information about the history of the early solar system. A study by scientists from the Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris, Université Paris Cité and CNRS, as part of an international consortium, reveals the isotopic composition of zinc and copper of asteroid Ryugu. The isotopic signatures show that Ryugu’s composition is close to Ivuna-like carbonaceous chondrites, and that Ryugu-like material from the outer solar system accounts for ~5-6% of Earth’s mass. These results are published on 12 December 2022 in the journal Nature Astronomy.
Meteorites found on Earth give scientists access to samples representing the first moments of the solar system. However, the return to Earth in December 2020 of the Hayabusa2 mission, operated by the Japanese space agency JAXA and bringing back 5 grams of fragments from the asteroid Ryugu, marks a major step forward by offering the possibility of analyzing samples unaltered by their arrival and stay on Earth. The first analyses, carried out by an international team, including researchers from the Institut de physique du globe de Paris, Université Paris Cité and the CNRS, have shown that the composition of the asteroid Ryugu is close to that of Ivuna-like carbonaceous chondrites (CI) – the most chemically primitive meteorites, and considered to have the composition closest to the Sun. However, some isotopic signatures (e.g., titanium and chromium) overlap with other groups of carbonaceous chondrites, so the details of the link between Ryugu and CI chondrites are not yet fully understood.
Zinc and copper are two moderately volatile elements, and are key elements to study the processes of accretion of volatiles during the formation of telluric planets. The different groups of carbonaceous chondrites show distinct zinc and copper isotopic compositions, with the CI chondrites being the more enriched in volatile elements. By carrying out additional analyzes of the zinc and copper isotopic composition of Ryugu, the scientists had access to a crucial tool for studying the origin of the asteroid.
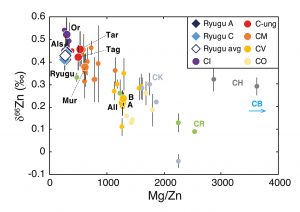
Zinc elemental and isotopic compositions for Ryugu and carbonaceous chondrites samples. (Source: Contribution of Ryugu-like material to Earth’s volatile inventory by Cu and Zn isotopic analysis, Marine Paquet, Frederic Moynier, Tetsuya Yokoyama et al., Nature Astronomy, 2022)
The international team showed, in a study published on December 12th, 2022 in the journal Nature Astronomy and led by Marine Paquet and Frédéric Moynier, cosmochemists at the IPGP, that the isotopic ratios of copper and zinc in the samples from Ryugu were identical to CI chondrites but different from all other types of meteorites. By finally confirming the similarity between Ryugu and CI chondrites, this study establishes that these primitive samples from Ryugu represent the best estimate of the solar composition to date for copper and zinc.
Finally, the zinc isotopic composition of Ryugu can also be used to study the accretional history of moderately volatile elements on Earth, which are essential for the development of planetary habitability. The study also demonstrates that the contribution of Ryugu-like material represents about 5% of the Earth’s mass.
> Bibliography:
Contribution of Ryugu-like material to Earth’s volatile inventory by Cu and Zn isotopic analysis, Marine Paquet, Frederic Moynier, Tetsuya Yokoyama et al., Nature Astronomy, 2022, DOI : 10.1038/s41550-022-01846-1
Read more

Prix Jeunes Talents France L’Oréal-UNESCO Pour les Femmes et la Science : Appel à candidatures 2026
La Fondation L'Oréal, en partenariat avec la Commission nationale française pour l'UNESCO et l'Académie des sciences, déclare officiellement ouvert l'appel à candidatures de l'édition 2026 du Prix Jeunes Talents France L'Oréal-UNESCO Pour les Femmes et la Science :...
read more
International Day of Women and Girls in Science: celebrating the women who push research forward
February 11 was the International Day of Women and Girls in Science. On this day, Université Paris Cité reaffirms its commitment to the equality between men and women and celebrates the journey of the women who advance research. Between celebrating our heritage and...
read more
Suivi des maladies chroniques : un patient sur deux serait ouvert à la téléconsultation
L’étude REACTIVE, coordonnée par la Dre Tiphaine Lenfant et le Pr Viet-Thi Tran et menée par des équipes de médecine interne de l’hôpital européen Georges-Pompidou AP-HP, du centre d’épidémiologie clinique de l’hôpital Hôtel-Dieu AP-HP, de l’Université Paris Cité, de...
read more
Journée internationale des femmes et des filles de science : célébrer celles qui font avancer la recherche
Le 11 février marque la Journée internationale des femmes et des filles de science. À cette occasion, l’Université Paris Cité réaffirme son engagement en faveur de l’égalité femmes-hommes et célèbre le parcours de celles qui font avancer la recherche. Entre un...
read more